Fundamental Analysis in Real-Time

Integrating fundamental analysis into real-time stock market analysis presents a unique challenge, requiring a sophisticated system capable of processing vast amounts of data rapidly and accurately. This involves combining traditional fundamental metrics with the dynamic nature of real-time price movements to generate actionable insights.Fundamental data, such as earnings reports, economic indicators, and company announcements, provides a long-term perspective on a company’s value.
Real-time price data, on the other hand, reflects the immediate market sentiment and the collective assessment of all available information. By combining these two data streams, a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of market dynamics can be achieved.
Integrating Fundamental and Real-Time Price Data
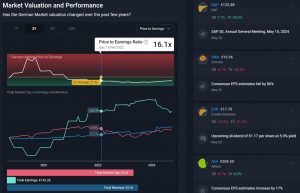
The integration of fundamental and real-time price data typically involves a multi-step process. First, real-time price data (e.g., stock price, volume, bid-ask spread) is collected and cleaned. Then, relevant fundamental data, such as earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings ratio (P/E), debt-to-equity ratio, and key economic indicators (e.g., GDP growth, inflation rate), are sourced and processed. Finally, these datasets are combined and analyzed using various quantitative methods, including statistical models and machine learning algorithms, to identify potential trading opportunities or to assess the impact of news events on stock prices.
For example, a sudden surge in trading volume coupled with a positive earnings surprise might indicate a strong buy signal.
Assessing the Impact of News Events on Stock Prices
News events significantly influence stock prices. The speed and accuracy of processing and interpreting this information are critical in real-time trading. Algorithmic approaches can be used to analyze news sentiment, classifying news articles as positive, negative, or neutral. This sentiment analysis can be combined with real-time price data to assess the market’s reaction to the news. For instance, an unexpectedly positive earnings announcement might trigger a sharp price increase, while negative news about a company’s product recall could lead to a significant price drop.
The speed of the reaction and the magnitude of the price movement provide valuable insights into the market’s sensitivity to the news.
Challenges of Incorporating Fundamental Analysis into Real-Time Trading
Incorporating fundamental analysis into real-time trading presents several challenges. The sheer volume of data to be processed and analyzed requires high-performance computing resources and efficient algorithms. The speed at which news events unfold and their impact on stock prices necessitate rapid data processing and interpretation. Moreover, the inherent uncertainty and noise in the market can make it difficult to accurately predict the impact of fundamental factors on stock prices.
Finally, the constant evolution of market dynamics requires continuous model calibration and refinement. For example, a model trained on historical data might become less accurate as market conditions change.
Interpreting Fundamental Data in Real-Time Market Movements
Interpreting fundamental data within the context of real-time market movements requires a nuanced understanding of both the underlying company fundamentals and the prevailing market sentiment. For example, a company reporting strong earnings might see its stock price decline if the overall market is experiencing a downturn due to broader economic concerns. Conversely, a company with weaker-than-expected earnings might see its stock price rise if the overall market sentiment is positive and investors are willing to overlook the company’s short-term performance.
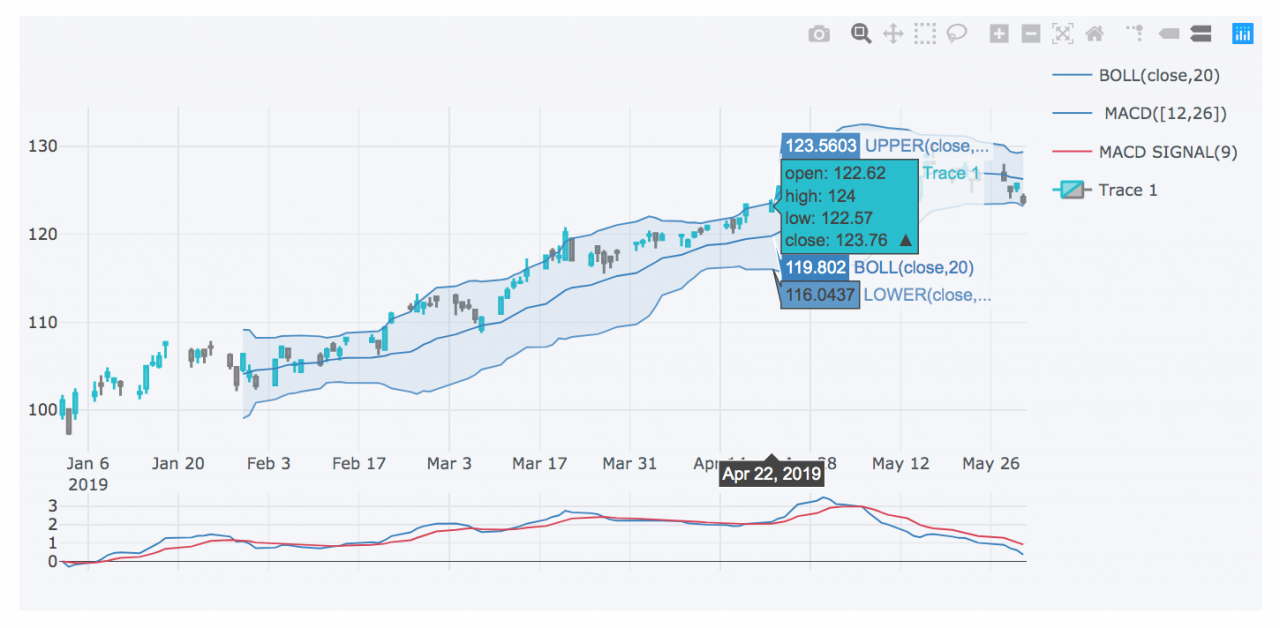
Real-time analysis necessitates a holistic view, considering both company-specific factors and macroeconomic trends. A strong understanding of technical analysis indicators alongside fundamental data is crucial for a comprehensive interpretation.