Risk Mitigation Strategies
Effective financial risk management isn’t just about identifying potential problems; it’s about proactively developing and implementing strategies to lessen their impact. This involves a multi-faceted approach tailored to the specific risks faced by the company. A well-defined mitigation plan significantly reduces the likelihood of financial distress and improves the overall financial health and stability of the organization.
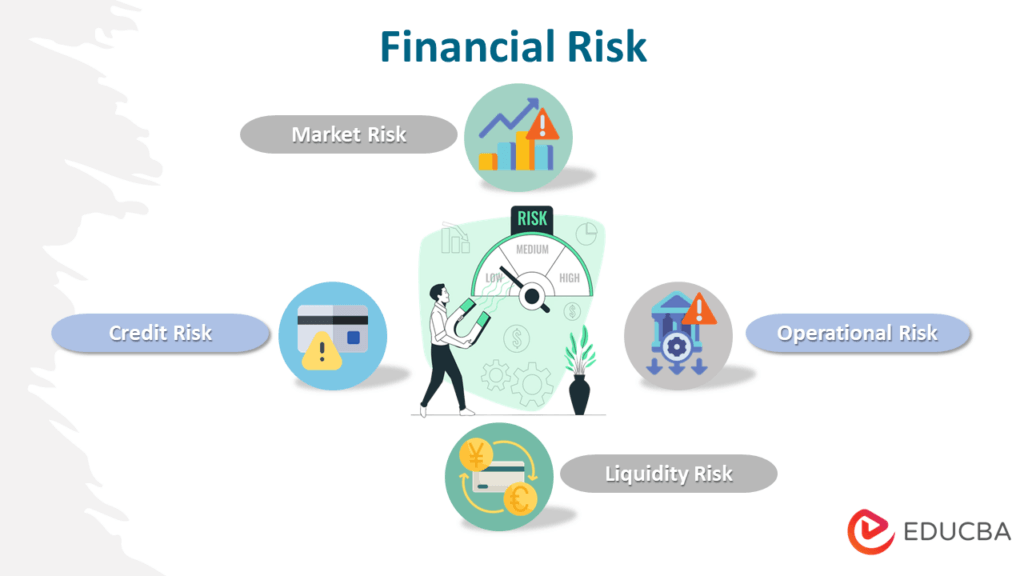
The selection of appropriate mitigation strategies depends heavily on the nature and severity of the identified risks. For instance, strategies to address credit risk will differ significantly from those used to manage market risk. A robust risk mitigation plan typically involves a combination of strategies, creating a layered defense against potential financial losses.
Credit Risk Mitigation Strategies
Credit risk, the risk of borrowers failing to repay their debts, is a significant concern for many businesses. Mitigation strategies focus on improving the creditworthiness of borrowers and reducing exposure to potential defaults.
- Diversification of Lending Portfolio: Spreading loans across various borrowers and industries reduces the impact of a single default. For example, a bank lending to diverse sectors (e.g., technology, manufacturing, healthcare) is less vulnerable than one heavily concentrated in a single sector susceptible to economic downturns.
- Credit Scoring and Analysis: Rigorous credit scoring and thorough due diligence on potential borrowers helps identify high-risk applicants and minimize the likelihood of defaults. This includes assessing financial statements, credit history, and industry trends.
- Collateralization: Requiring collateral, such as property or equipment, secures the loan and reduces lender losses in case of default. This minimizes the financial impact on the lender should the borrower fail to meet their obligations.
- Credit Insurance: Purchasing credit insurance transfers some of the credit risk to an insurance company, providing a financial safety net in case of borrower default. This is particularly useful for larger loans or loans to borrowers with less-than-perfect credit histories.
Market Risk Mitigation Strategies
Market risk, stemming from fluctuations in market prices (e.g., interest rates, exchange rates, commodity prices), requires strategies focused on hedging and diversification.
- Hedging: Using financial instruments like derivatives (futures, options, swaps) to offset potential losses from adverse market movements. For instance, a company expecting to receive a large payment in a foreign currency might use currency forwards to lock in a favorable exchange rate.
- Diversification of Investments: Spreading investments across different asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate) and geographic regions reduces the impact of market downturns in any single sector or region. This reduces the overall volatility of the investment portfolio.
- Value at Risk (VaR) Analysis: Using quantitative models to estimate potential losses in a given timeframe with a certain confidence level. This allows companies to understand their potential exposure to market fluctuations and adjust their strategies accordingly. For example, a VaR model might indicate a 95% chance of losing no more than $1 million in a month.
Operational Risk Mitigation Strategies
Operational risk encompasses the risk of losses due to internal failures or external events affecting business operations.
- Robust Internal Controls: Implementing strong internal controls, including segregation of duties, regular audits, and cybersecurity measures, minimizes the risk of errors, fraud, and disruptions. This includes procedures to verify transactions and safeguard sensitive data.
- Business Continuity Planning: Developing comprehensive plans to ensure business operations continue during disruptions (e.g., natural disasters, cyberattacks). This involves identifying critical business functions and developing backup systems and recovery procedures. For example, a company might have a backup data center in a different location to ensure continued operations in case of a disaster.
- Insurance: Obtaining appropriate insurance coverage (e.g., property insurance, liability insurance, cyber insurance) protects the company against unforeseen events and their financial consequences. This shifts the financial burden of unexpected events to the insurance provider.
Financial Risk and Corporate Governance

Effective corporate governance is the bedrock of sound financial risk management. A robust governance framework ensures accountability, transparency, and the implementation of appropriate controls to mitigate financial risks, ultimately protecting shareholder value and maintaining the company’s long-term stability. This section explores the interconnectedness of corporate governance and financial risk management, highlighting the crucial roles played by various stakeholders.
The Role of Corporate Governance in Financial Risk Management
Corporate governance provides the overarching framework within which financial risk management operates. It establishes clear lines of responsibility, defines decision-making processes, and ensures that appropriate resources are allocated to risk management activities. A well-defined governance structure fosters a culture of risk awareness and accountability, encouraging proactive identification, assessment, and mitigation of potential financial threats. This includes establishing clear policies and procedures, implementing effective internal controls, and regularly monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of the risk management framework.
The strength of a company’s governance directly impacts its ability to withstand financial shocks and maintain its financial health. For example, companies with strong governance structures, such as those with independent boards and robust audit committees, tend to exhibit better financial performance and lower risk profiles compared to their counterparts with weaker governance.
Responsibilities of the Board of Directors and Senior Management in Overseeing Risk Management
The board of directors holds ultimate responsibility for overseeing the company’s risk management framework. This includes approving the risk appetite, reviewing the effectiveness of the risk management processes, and ensuring that appropriate resources are allocated. Senior management is responsible for the day-to-day implementation of the risk management framework, including the identification, assessment, and mitigation of specific financial risks.
They are accountable for reporting risk exposures to the board and implementing corrective actions as needed. A clear division of responsibilities between the board and senior management is crucial for effective risk oversight. This often involves the establishment of risk committees, composed of both board members and senior managers, to provide focused oversight and expertise on risk management issues.
Companies like Johnson & Johnson, known for their strong ethical and governance standards, exemplify the importance of board oversight in shaping a proactive risk management culture.
Internal Controls and Effective Risk Management
Internal controls are the processes, policies, and procedures designed to ensure the reliability of financial reporting, the effectiveness and efficiency of operations, and compliance with laws and regulations. These controls play a vital role in mitigating financial risks by preventing errors, detecting fraud, and ensuring the accuracy and completeness of financial information. Examples of internal controls include segregation of duties, authorization procedures, reconciliations, and independent audits.
Robust internal controls are essential for maintaining investor confidence, preventing financial losses, and protecting the company’s reputation. A strong system of internal controls acts as a critical safeguard against a range of financial risks, including fraud, operational failures, and regulatory non-compliance. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (SOX) in the US, for instance, mandates the implementation of robust internal controls for publicly traded companies, demonstrating the regulatory emphasis on their importance.
Communication and Reporting Processes for Financial Risks
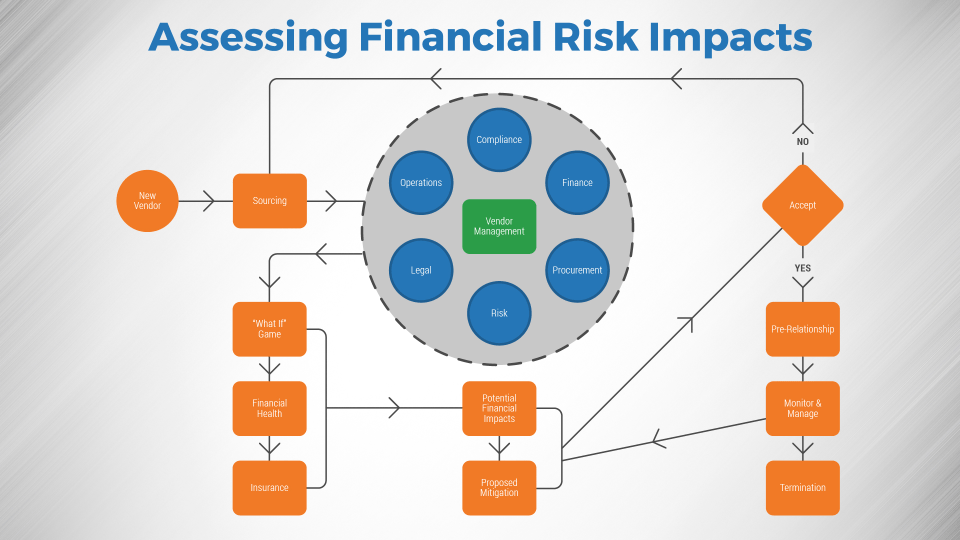
Effective communication and reporting are essential for ensuring that financial risks are identified, assessed, and mitigated effectively. A well-defined communication and reporting process ensures that relevant information flows smoothly between different levels of the organization, from operational staff to senior management and the board of directors. This process should include regular reporting on key risk indicators, timely escalation of significant risks, and clear communication of risk mitigation strategies.
A visual representation of this process can be beneficial.